Modified accelerated mortar test for testing
the ASR expansion potential
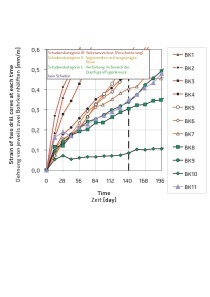
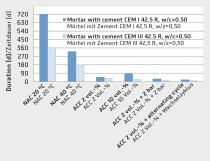
Direct testing of the alkali-silica reactivity that causes damage in concrete generally involves a very time-consuming process, since the concrete specimens have to be stored in a cloud chamber for several months. To abbreviate this test period, a modified accelerated mortar test was developed at the scientific-technical institute WTI Unterwellenborn to determine the ASR potential in the concrete. This new test was calibrated and compared in tests carried out by the method recommended by the DAfStb [1].
To investigate the ASR in structural concretes and the alkali reactivity in fresh concretes as well as in concretes containing various additions, cements, etc., only the aggregate, among other things, is hitherto used as a basis. The effectiveness of the cements used in a given case is assessed in connection with their alkali contents as well as with their puzzolanic constituents. Direct testing of the ASR potential in the hardened concrete is then performed on the basis of the “Recommendation for damage diagnosis and repair” for structural concrete published by the DAfStb [1]. For this...