Concrete 4.0 – Self-learning digital production techniques for sustainable concrete
The European Union has adopted the Green Deal to make Europe climate-neutral by 2050 and to minimize the use of primary resources. The construction industry is exceedingly resource-intensive and emits about 40 percent of the greenhouse gases in Germany alone, which is why it plays a crucial role in achieving this goal. Important building blocks for decarbonizing the industry include a targeted reduction in cement consumption, but also the efficient use of secondary raw materials such as recycled concrete.
The key to significantly increasing the ratio of recycled concrete and other previously unused residual materials in concrete production
lies in developing technologies that make it possible to capture and compensate the influence of variations in the characteristics of concrete raw materials on the finished product continuously in order to optimize its cost efficiency and environmental footprint.
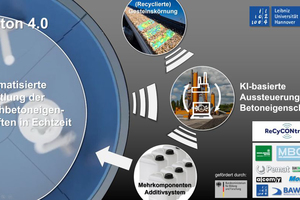
The ReCyCONtrol collaborative research project aims to increase the sustainability and resource efficiency of the concrete production process significantly by creating the technical prerequisites for using
raw materials that were previously unsuitable due to excessive variations in their properties. This goal is achieved by introducing automated, self-learning process monitoring and control methods in concrete production. Applying such methods previously unknown in the concrete industry should make it possible to dispense with the ubiquitous large allowances for deviation required for quality control reasons.
At the heart of the consortium’s work is the development of novel methods based on sensor data that make it possible to capture the characteristics of the input materials and of the fresh concrete in real time. This information creates the basis for developing self-learning control loops relying on artificial intelligence (AI) methods.
Any concrete characteristics deviating from the defined target values can then also be managed and controlled in real time using a multi-component additive system. Combining these techniques allows for the safe use of a significantly wider range of recycled materials in concrete production while saving cement thanks to an efficient quality control scheme implemented for the concrete.