World’s first system for fully automated cutting and handling of reinforcing steel mesh
Manual labor is still the rule rather than the exception in many areas. Terhoeven GmbH & Co. KG has recently found a solution for a typical work example: the monotonous, laborious cutting of reinforcing steel mesh. The medium-sized machine manufacturer relies on equipment supplied by Mitsubishi Electric and the automation expertise of Orgassa GmbH.
In the production of reinforcing steel mesh, steel wire is first unwound from a coil and straightened, which also lends the typical ribbed texture to the rebar. An automated machine then welds the wires together to form a mesh of transverse and longitudinal bars. To ensure optimal plant utilization, the welding machine produces the mesh in the maximum possible dimensions. Since smaller sizes are usually required on construction sites, this mesh needs to be cut to the right size. This process has previously been very labor-intensive since there was no automated solution. Up to six people are needed to lift the heavy pieces of mesh and position them on the cutting machine. During the subsequent stacking process, every second mesh needs to be turned over to reduce the stack height. It is becoming increasingly difficult to find staff for this strenuous and monotonous work.
A company, which processes 3,400 tons of rebar per day, was thus seeking an automated solution.
Equipment manufacturer specializing in reinforcing steel mesh
The company found what they were looking for at Terhoeven GmbH & Co. KG, which provides mechanical engineering solutions for this sector under the Hambi brand. Founded in 1908 as a village smithy, the company is currently being managed by Stephan Terhoeven, who represents the fourth generation of the Terhoeven family: “Since 2006, we have been concentrating entirely on mechanical engineering while discontinuing our other business lines in agricultural machinery.” Employing about 30 people, Hambi supplies a variety of machines for handling, cutting, and bending reinforcing steel mesh. This range includes small bending benches designed for on-site use, but also large machines for bending shops and mesh manufacturers.
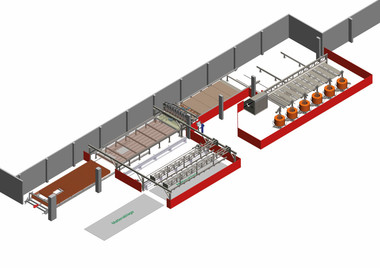
On behalf of the customer, the equipment manufacturer developed a system that handles, cuts, and stacks reinforcing steel mesh in a fully automated process. The automated cutting system first separates the top mesh from the stack, lifts it, and conveys it to the feed unit, which pushes the mesh into the guillotine shear until the set length is reached. The shear then cuts the mesh, and the mesh ejector transports the cut section to the mesh turning device. In the last step, the system stacks the individual pieces of mesh. In this process, the mesh turning device turns over every second mesh. This turning step minimizes stack height since the sections are nested inside each other.
Separating and lifting the mesh poses a challenge
Lifting the top mesh from the stack appears to be relatively simple at first glance. “However, this step is a major challenge for automation,” explains Stefan Broeckmann, who oversees design and development at the equipment manufacturer. Manufacturing tolerances of reinforcing steel mesh are in the centimeter range, yet its handling requires accuracy of less than one millimeter. In addition, the individual pieces of mesh do not lie neatly in the stack. The company commissioned Orgassa GmbH to implement the automated solution. “We have a long-standing, trusting work relationship,” says Stephan Terhoeven. The first important step is to determine the actual position of the mesh and the corresponding points at which the grippers can lift the mesh. Marc Orgassa, Managing Director of Orgassa GmbH, outlines the process: “Image processing combining state-of-the-art camera equipment with laser sensors detects the actual position of the gripping points so that the mesh can be gripped exactly where needed.” Orgassa GmbH programmed the entire 3D image processing software used for this purpose.
The next challenge arises when the six grippers lift the reinforcing steel mesh. During lifting, the mesh will sag, causing horizontal forces to act on the lifting gear. “To compensate for this,” explains Marc Orgassa, “the distances between the individual pick-up points need to be adjusted. Three separately operated drives are thus required for each of the six points to move the grippers in all three spatial dimensions. During operation, drives must be controlled precisely and synchronously.”
Drive and automation equipment from a single source
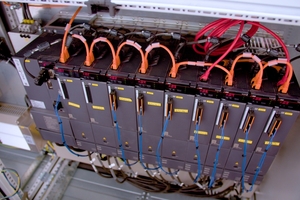
To compensate for the deflection of the mesh during lifting, 18 drives are required for the six grippers, plus four additional drives for conveying the pieces of mesh within the system and turning them before stacking. Servo drives from Mitsubishi Electric with corresponding servo amplifiers are used in each case. The MR-J5 series motors are very compact and provide a highly dynamic performance. The associated servo amplifiers can be coupled via intermediate circuits – the braking energy of one drive can thus be used directly for another drive. The servo amplifiers also allow for energy recovery. Overall, the system thus achieves a high level of energy efficiency. “The motion controller enables us to optimally implement the required drive synchronization,” Marc Orgassa cites an important reason for choosing this system. All other automation components and units to ensure power supply to the entire system were also sourced from Mitsubishi Electric.
Occupational safety a top priority
When handling the heavyweight reinforcing steel mesh, automation must ensure the safety of operating personnel. This is why all drive and automation equipment components are designed with safety in mind. Besides the safety PLC, this also applies to the servo drives, which are also monitored for safety. In the event of a power outage, drives will always stop in a safe position. This position is also monitored by encoders designed for maximum safety.
Single-person operation
The automated cutting system is operated via a GOT control unit from Mitsubishi Electric. In addition to the touchscreen, several buttons and switches are also integrated to facilitate operation with gloves. Marc Orgassa used the iQ programming environment to program the user interface and visualization system. The software package enables efficient cross-system programming of all automation components, including the drives, the safety PLC, and the operating unit. “The only exception was the image processing software, which we programmed in C,” Marc Orgassa adds.
System commissioned successfully
After a development phase of almost two years, the first system was commissioned at the customer’s premises in spring 2024. “The automated cutting system is six meters high and over 40 meters long,” says Stefan Broeckmann, outlining the system’s enormous dimensions. Stephan Terhoeven explains quite simply why Mitsubishi Electric was the supplier of choice for the drive and automation equipment: “We have been using Mitsubishi Electric products in our machines and systems for many years and have had consistently good experiences with them.” Marc Orgassa adds: “According to our experience, it makes a lot of sense to obtain all components from a single source. And with Mitsubishi Electric’s current portfolio, we can easily implement real-time communication, drive synchronization, and required safety features.”
Following the world’s first successful automation of the cutting of reinforcing steel mesh, the equipment manufacturer is already working on the next steps. For example, a machine is currently under development for bending reinforcing steel mesh into cages in various geometries and sizes, which will be used on-site to produce columns, beams, or columns. As a matter of course, this system will again work fully automatically. “When it comes to automation equipment, we will certainly rely on Orgassa and Mitsubishi Electric systems again,” says Stephan Terhoeven.
CONTACT
Terhoeven GmbH & Co KG
Hermesweg 1-7
47665 Sonsbeck-Hamb/Germany
+49 2838 9138-0
Mitsubishi Electric Europe B.V.
Niederlassung Deutschland
Mitsubishi-Electric-Platz 1
40882 Ratingen/Germany
+49 2102 486-0
Ats Orgassa GmbH
Im Niederbruch 24
46509 Xanten/Germany
+49 2801 4019