Punching shear behavior of steel fiber reinforced flat slabs in combination with punching shear reinforcement
The guideline “Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete” published by the German Committee for Reinforced Concrete (DAfStb) in 2012 regulates the punching shear design of steel fiber reinforced flat slabs with and without punching shear reinforcement in Germany. The punching shear design of flat slabs without shear reinforcement is herein comprised as an additive design approach, consisting of the concrete contribution of a flat slab without shear reinforcement and the steel fiber contribution dependent on the post-cracking tensile strength of the steel fiber reinforced concrete. Regarding the punching shear design of flat slabs with shear reinforcement, the combination of the two contributions, steel fibers and punching shear reinforcement, is explicitly excluded due to a lack of ex-
perience and investigations. The national and international literature shows only eight steel fiber reinforced tests with punching shear reinforcement. These were either carried out with for Germany untypical punching shear reinforcement or failed due to bending in the test. Based on these experiments, no conclusions regarding the effectiveness and load-bearing behavior of steel fiber reinforced flat slabs in combination with punching shear reinforcement can be drawn.
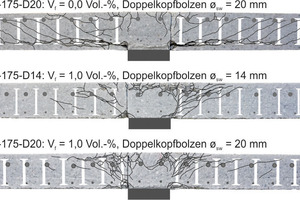
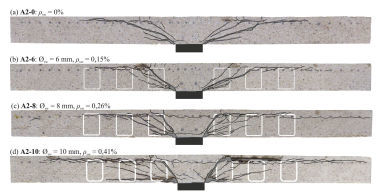
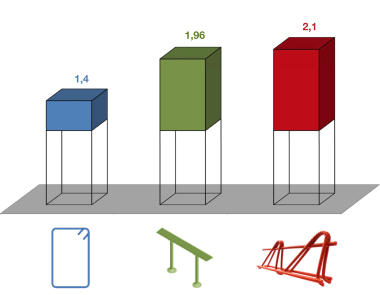
For the systematic investigation of the punching shear capacity of steel fiber reinforced flat slabs with closed stirrups and shear studs as punching shear reinforcement, two series with three tests each were carried out. The results obtained show the potential for improving the punching shear capacity and permit the description
of the load-bearing behavior. Simplified, a theoretical load is calculated as the sum of the concrete and steel fibre contribution according to the DAfStb guideline “Steel fibre reinforced concrete” and the steel contribution according to DIN EN 1992-1-1+NA(D). Comparing this theoretical load with the experimental load allows to evaluate the validity of this simplified approach.