(10) WO 2012/162292 A2
(22) 22 May 2012
(43) 29 November 2012
(71) PREMIER MAGNESIA, LLC [US/US]; 300 Barr Rarbor Drive, Suite 250, West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania 19428 (US)
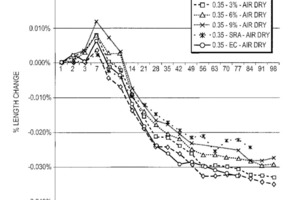
(57) Portland Cement-based concretes and mortars exhibit significant reduction in shrinkage cracking when combined with Magnesium Oxide (MgO), Shrinkage Reduction Admixtures (SRA) and Super Absorbent Polymers (SAP). However, MgO isasolid that reacts with water, SRA is a liquid, and SAP if not added properly could pull water out of the system and thus increase shrinkage. Unique admixture blends used as supplementary cementing...