Acid resistance of concrete – Multi-site comparisons of performance test methods
Any performance-based durability design will inevitably require reliable, reproducible performance criteria. However, there is not yet a uniform or standardized test method for assessing the acid resistance of concrete. Instead, a number of methods were developed that differ in terms of their test conditions and assessment criteria. This is why test results of different studies cannot be compared to each other and sometimes even lead to contradictory conclusions.
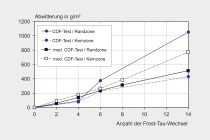
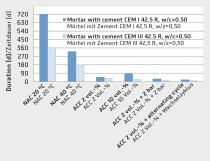
Given this situation, multi-site investigations were carried out as part of the AiF/IGF collaborative research project on “Performance-based Design for Chemical Attack on Concrete” in order to compare four different performance test methods. It was found that the comparability and reproducibility of test results is not primarily dependent on the selected measuring equipment or test setup. Rather, the defined test conditions and the precision with which they are managed and controlled play a crucial role in this regard. [1] already identified acid concentration and saturation as well as the homogeneity of the test medium as the key test parameters. This approach makes it possible to generate a similar exposure conditions for any test setup, which leads to comparable corrosion kinetics and thus makes test results comparable and reproducible. It is thus possible, on the basis of these clearly defined requirements for test parameters – as described, for instance, in [1] –, to make existing test methods comparable and to standardize the acid resistance testing of concrete. In addition, the investigations showed that generally accepted and frequently applied test methods are not always reproducible and may even lead to incorrect conclusions.