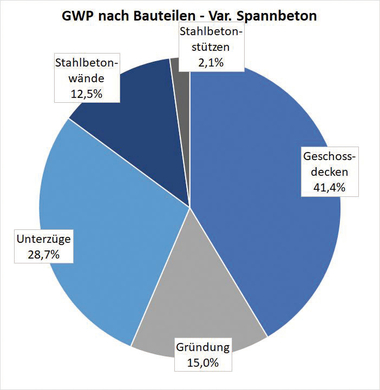
Explanation of the DafStb code of practice “Concrete floor slabs and roofs made of precast hollowcore slabs”
The DafStb code of practice “Concrete floor slabs and roofs made of precast hollowcore slabs,” with date of issue January 2023, has been published by Beuth-Verlag in Berlin in three parts:
Part 1: Planning, design and implementation of concrete floor slabs and roofs with reinforced-concrete hollowcore slabs
Part 2: Planning, design and implementation of concrete floor slabs and roofs with prestressed hollowcore concrete slabs
Part 3: General requirements.
Inclusion is intended of the hollowcore code of practice in the model for administrative regulation in technical construction Regulations (Muster-Verwaltungsvorschrift Technische Baubestimmungen, MVV TB). The code of practice supplements the existing regulations for simplified verification in planning and design, and provides recommendations for application of precast prestressed-hollowcore slabs in concrete floors and roofs.
The precast hollowcore slabs are prestressed-concrete elements with prestressed tendons. The construction method with prestressed hollowcore concrete slabs has the following specific characteristics:
The slabs exclusively contain prestressing tendons in the form of strands and wires (i.e., no reinforcing steel) and feature continuous hollowcores over the length of the slabs;
For shear-force design, distinction is made between rigid support of the slabs (e.g., on a wall) and flexural support of the slabs (e.g., on a steel beam);
The following step is crediting the tensile strength of the concrete required for assuming the front-end tensile stresses during introduction of tensioning forces for absorbing shear-force stresses in webs and for absorbing bending stresses in transverse directions of the slabs.
The lecture explains verification formats for the ultimate limits of supporting capacity and for ultimate limits of serviceability. Also included are instruction on mating slabs, the design of floor diaphragms and implementation at the construction site.